Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor详解
约 915 字大约 3 分钟
Java并发
2024-03-02
1. ThreadPoolExecutor参数
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}根据如上构造方法,在new一个ThreadPoolExecutor时需要传入如下参数
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(properties.getCorePoolSize(),
properties.getMaxPoolSize(),
properties.getKeepAliveTime(),
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(properties.getBlockQueueSize()),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
handler);1)核心线程数:corePoolSize
任务队列未达到队列容量时,最大可以同时运行的线程数量为corePoolSize。
(2)最大线程数:maxPoolSize
任务队列已满,此时可同时运行的线程数量变为maxPoolSize。
(3)等待时间keepAliveTime
线程池中的线程数量大于corePoolSize,如果没有新任务提交,核心线程外的线程不会立刻销毁,会等待keepAliveTime再被回收销毁。
(4)参数的时间单位:unit
一般是TimeUnit.SECOND
(5)阻塞队列:workQueue
(6)拒绝策略:handler
2. 线程池处理任务流程
其中ThreadPoolExecutor#execute()方法的处理逻辑: 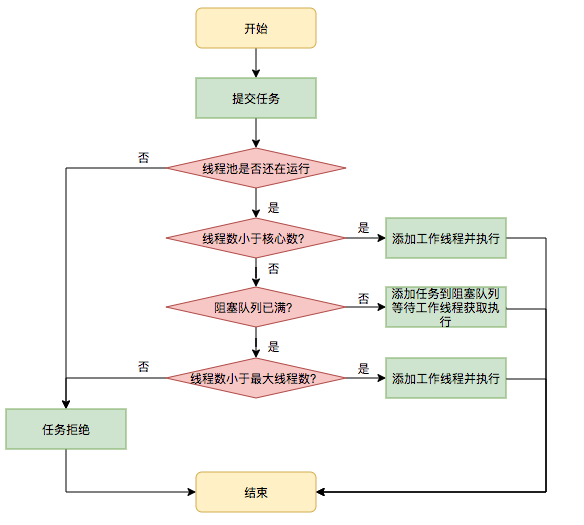
public void execute(Runnable command) {
//1、判断是否传进来线程
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
//2、判断工作线程池是否满了
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
//3、判断工作队列是否满了
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
//4、以上条件都不符合,直接拒绝
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}结合上述参数,线程池处理任务的流程可以这样描述。
- 1.提交任务,判断核心线程池是否已满,如果没有满(当前线程数 < corePoolSize),则创建线程
- 2.如果核心线程池已满,但没达到最大线程数(corePoolSize <= 当前线程数 < maxPoolSize),则把该任务放到阻塞队列里等待执行
- 3.如果阻塞队列已满,但当前线程数 < maxPoolSize,则新建一个线程来执行任务。
- 如果当前线程数 >= maxPoolSize,那么会根据拒绝测觉拒绝提交的任务。
线程池拒绝策略(handler)
当线程池的线程数达到最大线程数时,需要执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略需要实现 RejectedExecutionHandler 接口,并实现 rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) 方法。不过 Executors 框架已经为我们实现了 4 种拒绝策略:
拒绝策略
1.AbortPolicy:丢弃任务并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。
2.CallerRunsPolicy:由调用线程处理该任务。
3.DiscardPolicy:丢弃任务,但是不抛出异常。可以配合这种模式进行自定义的处理方式。
4.DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列最早的未处理任务,然后重新尝试执行任务。